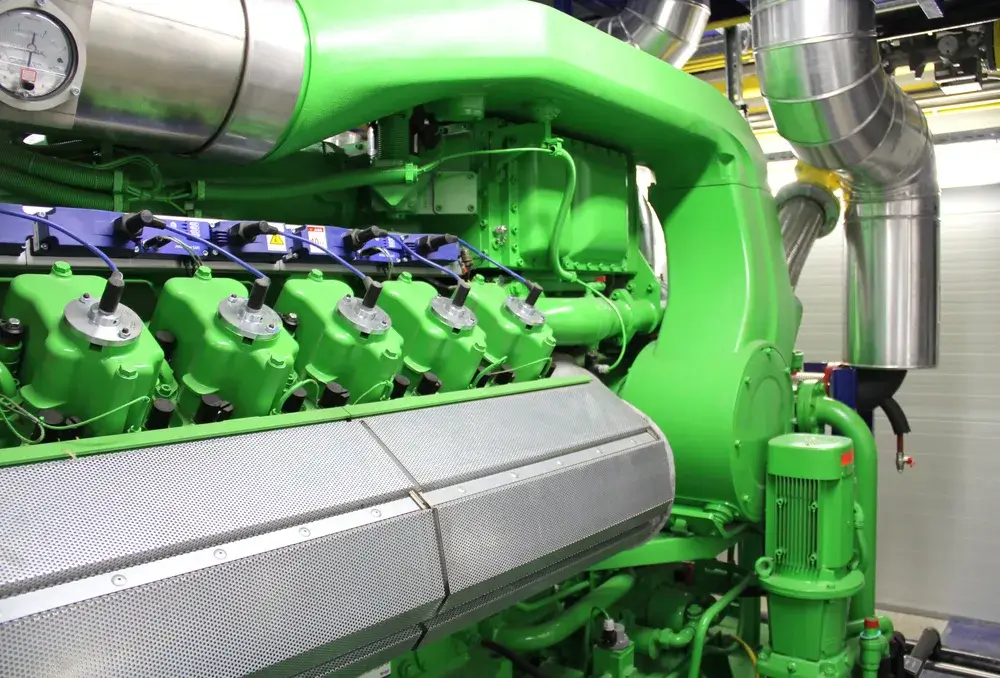
The Advantages of Captive Power Plants

Captive power plants offer a strategic advantage for businesses by ensuring a reliable, cost-effective, and sustainable energy supply. These facilities, designed for exclusive use by the owning entity, not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to environmental conservation through the adoption of cleaner energy sources.
How do Captive Power Plants work?
Captive power plants operate as private electricity generation facilities owned by individual businesses or entities, primarily for their own use rather than for public distribution.
Everything you need to know about Captive Power Plants
Captive Power Plants (CPPs) are energy solutions tailored for the exclusive benefit of their owners or operators to provide a dependable and economical source of power. This article delves into the comprehensive world of Captive Power Generation, covering all you need to know about Captive Power Plants, their benefits and drawbacks, the variety of fuels they can utilize, and the reasons behind their popularity.
These plants enable organizations to produce energy directly tailored to their operational needs, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply. This self-sufficiency in electricity generation allows businesses to reduce dependency on national or regional power grids, offering a significant advantage in regions where public power supply is unreliable or expensive.
Types of Captive Power Plants
Captive power plants come in various types, distinguished primarily by their fuel sources. These can range from conventional fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas to renewable sources like solar and the biogas industry.
Each type has its unique setup and operational requirements, catering to the diverse energy needs and environmental goals of businesses. For instance, coal-based plants are known for their robust output, while renewable energy-powered plants emphasize sustainability and reduced carbon footprint, offering flexibility in how companies approach their energy production strategies.
Economic Advantages
The economic advantages of captive power plants are significant, encompassing cost savings through reduced electricity charges and fuel consumption efficiencies. These plants enable businesses to predict and manage energy costs more effectively, shielding them from market volatility and high prices associated with external power supplies.
Additionally, by generating their own power, companies can achieve a faster return on investment, thanks to lower operational costs and the potential for selling excess power back to the grid, further enhancing their economic benefits.
Reliability and Energy Security
Captive power plants significantly enhance reliability and energy security for businesses, providing a stable and consistent power supply. This is crucial in areas where the public grid is unreliable, ensuring operations are not disrupted by power outages or fluctuations.

Moreover, having direct control over power generation means companies can quickly adapt to changes in demand, further securing their energy supply and maintaining uninterrupted business processes. This reliability supports not just day-to-day operations, but also long-term planning and growth strategies.
Control and Flexibility Over Energy Production
Captive power plants offer businesses high control and flexibility over their energy production, allowing them to tailor their power generation to meet specific operational demands. This control enables companies to optimize energy consumption, improve efficiency, and adjust production in real time based on their current needs.
Such flexibility not only enhances operational capabilities but also allows businesses to implement more sustainable and cost-effective energy management strategies, aligning closely with their financial and environmental objectives.
Environmental Benefits
Captive power plants offer big environmental benefits by enabling businesses to utilize cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. This shift towards renewable energy sources like the biogas industry, solar and wind industry reduces dependence on fossil fuels, thereby decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to a healthier environment.
Additionally, the localized production of energy minimizes transmission losses and promotes more efficient use of resources, further underscoring the environmental advantages of captive power systems.
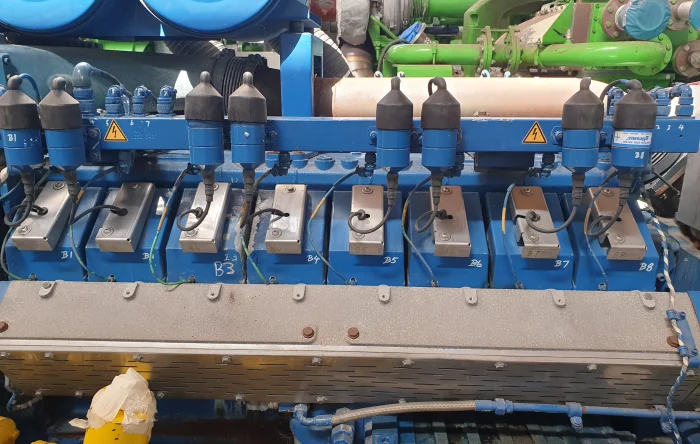
PowerUP is your partner for Captive Power Plants
PowerUP provides an extensive array of gas engine services and high-quality gas engine spare parts tailored for engines used in Captive Power Plants, aimed at enhancing their operational efficiency and reliability.
This support covers everything from gas engine repair to gas engine upgrades, condition based overhaul and both field service and remote service, ensuring that your energy systems remain in peak condition.
Frequently asked questions
What is a captive power plant?
A captive power plant is a facility that generates electricity primarily for the personal use of the entity that owns it, rather than supplying power to the public grid.
Can captive power plants use renewable energy sources?
Yes, captive power plants can utilize various renewable energy sources, including biogas solar and wind, to generate electricity, promoting sustainability.
How do Captive Power Plants integrate with grid-connected distribution systems?
Captive Power Plants can integrate with grid-connected distribution systems to sell surplus power back to the grid or exchange power during periods of low generation. This integration involves meeting regulatory standards and technical requirements to ensure safety, reliability, and compatibility with the grid infrastructure.
What are the main economic benefits of operating a captive power plant?
Key economic benefits include cost savings on energy, more predictable energy pricing, and the potential for additional revenue through selling excess power.
How do captive power plants enhance energy security?
They provide a reliable and consistent energy supply, reducing dependency on external power sources and mitigating the impact of grid unreliability.