The operation of a biogas plant

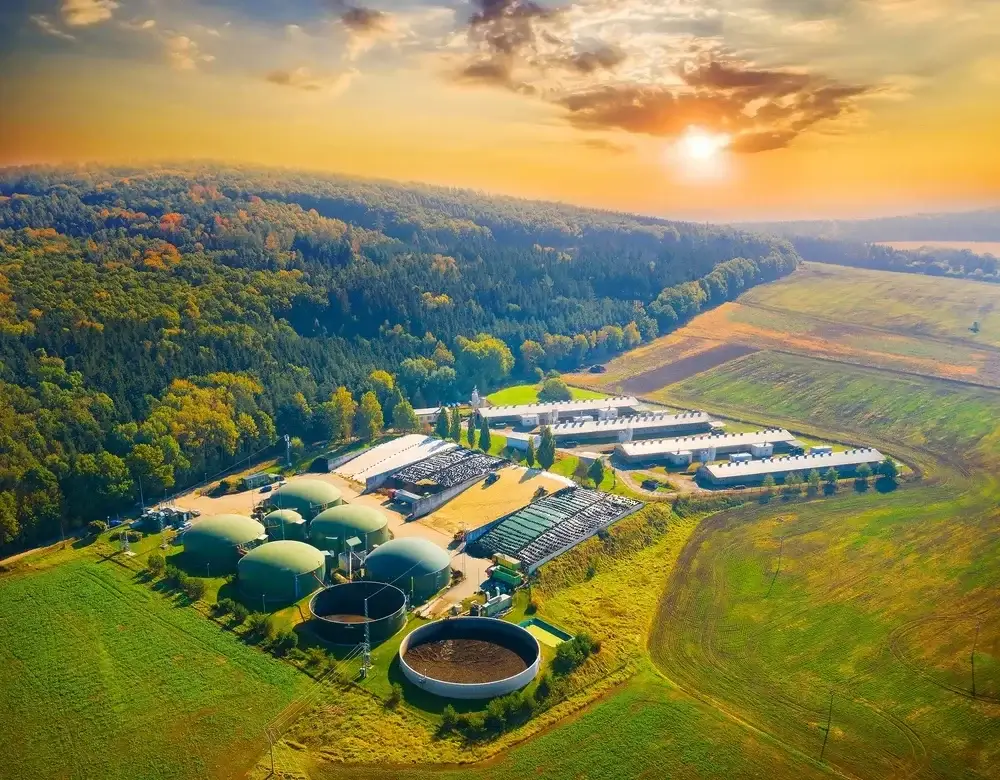
Biogas plants are an intriguing example of innovative technology that not only contributes to energy production, but also offers significant ecological and sustainable advantages. These plants convert organic materials like manure, fertilizer, bio-waste, and energy crops into valuable biogas, which can be utilized as a renewable energy source.
However, how does a biogas plant function, and how does it contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gases and the production of sustainable energy for the biogas industry? In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of how biogas plants work and examine their role more closely in modern energy infrastructure. As experts with over 10 years of experience in the field, PowerUP provides you with sound insights into how biogas plants work – read on to discover more!
Anaerobic fermentation
This is a natural process in which organic materials are broken down without the presence of oxygen. In a specialized container called a fermenter, materials such as manure, fertilizer, bio-waste, and energy crops are placed. Microorganisms break down these organic raw materials and convert them into biogas, while excluding oxygen.
This biogas primarily consists of methane and carbon dioxide and serves as a valuable source of energy. Anaerobic digestion is therefore the crucial step in the efficient and sustainable production of biogas in a biogas plant.
Types of materials used in biogas plants
The diversity of feedstocks and raw materials in biogas plants is impressive. Commonly used materials include manure and fertilizer, which are produced in large quantities in agriculture. Additionally, organic waste from households and industry, digestate from food processing, as well as specifically cultivated energy crops such as corn or grass, are also introduced into the fermenter.

Even residual materials and renewable raw materials can be used as feedstocks. This broad range of raw materials enables flexible adaptation to available resources and ensures that biogas plants can make a significant contribution to waste recycling and the sustainable utilization of renewable resources.
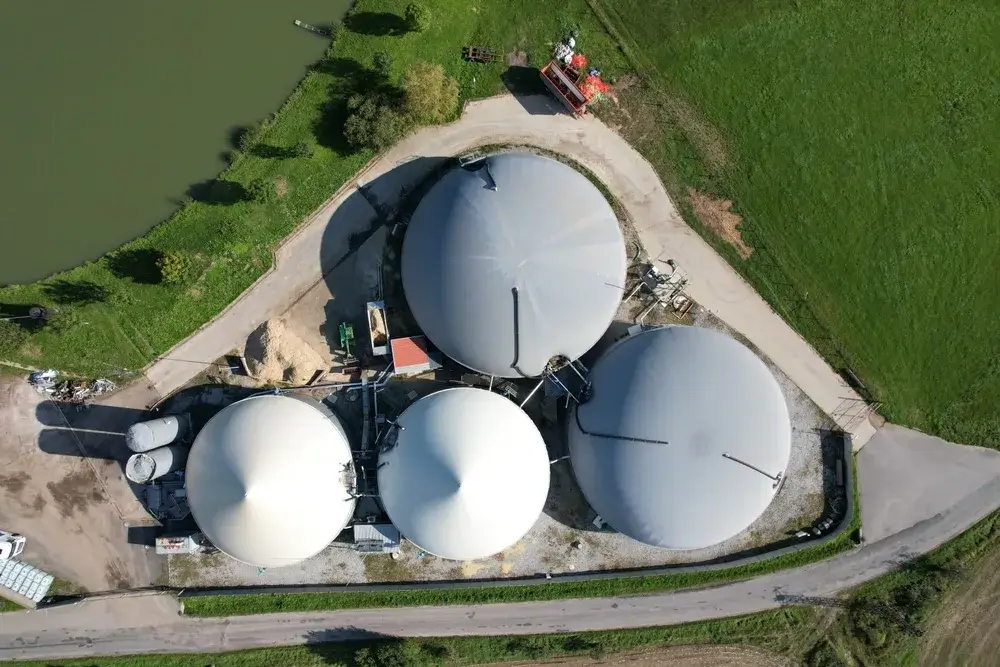
The fermenter
The fermenter plays a central role in the operation of a biogas plant. It is the place where the anaerobic fermentation of organic materials takes place. This specialized container ensures optimal conditions for the microorganisms to efficiently convert the raw materials into biogas.
There are various types of fermenters, including continuous and batch systems. The choice of the right fermenter design depends on various factors, including the type of raw materials used and the desired process control. In any case, the fermenter is where the magic of biogas production happens and paves the way for sustainable energy provision.
Following the fermentation process, the remaining fermentation residues and by-products in biogas plants emerge as a nutrient-rich resource, ideal for use as organic fertilizer in agriculture.
Gas production and processing
After the anaerobic digestion has taken place in the fermenters and the biogas has been generated, it needs to undergo purification in order to achieve the desired quality. This process involves the removal of impurities such as hydrogen sulfide and water, in order to produce biomethane that meets the quality requirements for injection into the natural gas grid.
The purification process enables the versatile utilization of biogas and contributes to the sustainable integration into existing energy infrastructures.
Biogas as an energy source
Biogas is an incredibly versatile energy source and the primary product of biogas plants. It primarily consists of methane, which can be utilized as a renewable energy source. One common application of biogas is in combined heat and power plants (CHP), where it is burned to generate both electricity and heat, resulting in high energy efficiency.
In addition to electricity generation, biogas can also be used as a fuel in vehicles, thereby reducing the use of fossil fuels. The simultaneous utilization of waste heat from the process makes biogas an extremely efficient energy source. The versatility of biogas contributes to the diversification of energy sources and the reduction of environmental impact, and it plays a significant role in sustainable energy supply.
Integration into the energy system
The integration of biogas into the national natural gas grid is a crucial step towards the sustainable utilization of renewable energies. Biomethane, derived from processed biogas, meets the quality standards necessary for injection into the natural gas grid. This facilitates the seamless integration of biogas into existing energy infrastructures.
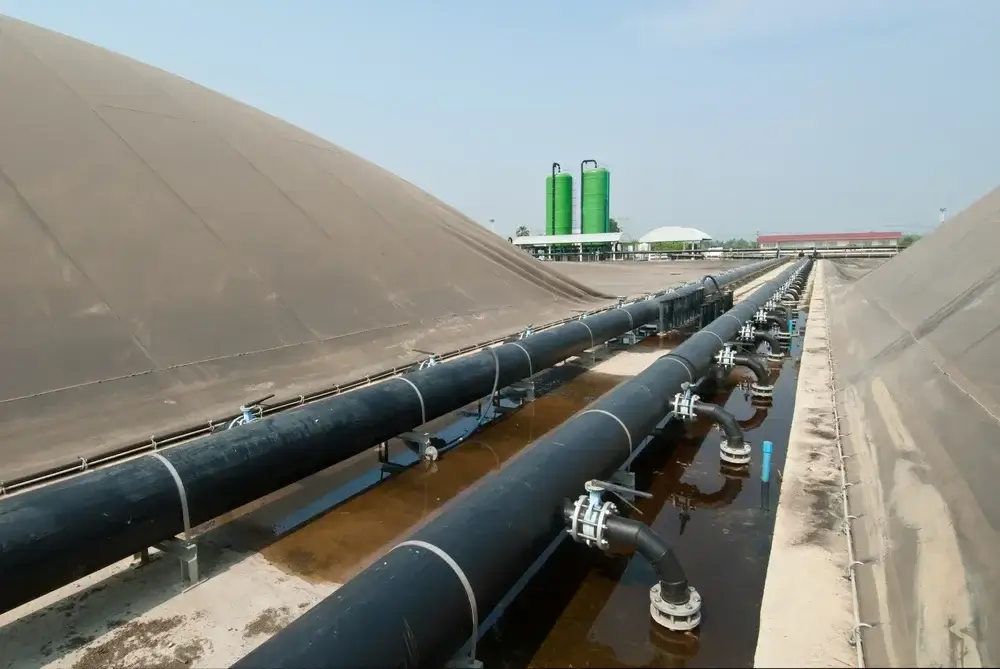

The biomethane that is fed in can then be utilized for decentralized power generation, heat supply, or as fuel for vehicles. This integration into the energy system contributes to reducing the dependence on fossil fuels and incorporating renewable energies into the energy supply.
Bring the operation of your biogas plant to the next level – with PowerUP
Enhance your operations with PowerUP. We offer a selection of gas engine spare parts and gas engine services, including engine upgrades, condition based overhauls and gas engine repairs for engines like MWM® and Jenbacher®, aimed at improving efficiency and dependability. Choose PowerUP for professional solutions that streamline your operations.