What is Captive Power Generation?

Captive power generation offers businesses a self-reliant alternative to traditional grid power, enabling more control over energy sources and costs. This approach involves generating electricity through private facilities specifically for the use by the company that owns them.
In this article, we will explore what captive power generation is, how it operates, and its benefits and challenges.
An Introduction to Captive Power Generation
Captive power generation refers to the process where businesses or industrial entities generate their own electricity to meet their specific operational needs, independent of the public power grid. This system allows companies to ensure a consistent energy supply, especially in regions where public utilities are unreliable or expensive.
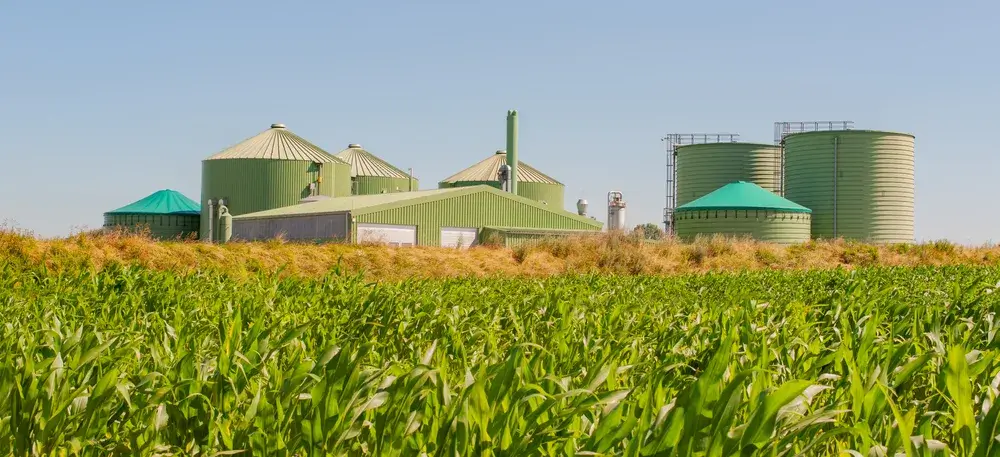
Captive power plants (CPP plants) can use a variety of fuels, including natural gas, biogas or coal, tailoring energy production to economic and environmental strategies.
Everything you need to know about Captive Power Plants
Captive Power Plants (CPPs) are energy solutions tailored for the exclusive benefit of their owners or operators to provide a dependable and economical source of power. This article delves into the comprehensive world of Captive Power Generation, covering all you need to know about Captive Power Plants, their benefits and drawbacks, the variety of fuels they can utilize, and the reasons behind their popularity.
Types of Captive Power Plants
Captive power plants can be categorized based on the type of fuel they use, which directly influences their design and operational strategy. Common types include natural gas and renewable energy forms like biogas plants, solar or wind. Additionally, there are hybrid systems that combine multiple fuel sources to enhance reliability and reduce environmental impact.
Each type has distinct advantages and considerations, making them suitable for different industrial applications depending on factors such as local fuel availability, environmental regulations, and energy needs.
How Captive Power Plants operate
Captive power plants operate by generating electricity primarily for the consumption of the entity that owns them, not for sale to the public. This self-generation is achieved through facilities that are often located on-site or near the site of the entity where the power is consumed.
These plants are designed to ensure a reliable, cost-effective, and often more environmentally friendly supply of energy. They can operate continuously or be used as a backup system during times of grid failure or peak demand periods, thus providing energy security and operational independence.
The Benefits and Challenges of Captive Power Generations
Captive power generation offers notable benefits and comes with certain challenges:
Benefits:
- Reliability: Ensures a steady supply of power, which is crucial for operations in areas with unreliable grid services, thereby preventing production losses due to power outages.
- Cost Control: Reduces dependency on utility providers, so operational costs can be controlled and predicted, protecting businesses from fluctuating energy prices.
- Energy Efficiency: Captive plants can be designed to use waste heat for heating or industrial processes, and therewith significantly increasing overall energy utilization and reducing waste.
Challenges:
- High Initial Investment: The initial setup for captive power plants requires significant capital investment for equipment and infrastructure.
- Maintenance: Requires a dedicated operational team (or a partner company) with the necessary expertise to manage and maintain complex machinery to ensure smooth operation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Must adhere to strict environmental and safety regulations, which can involve complicated permitting processes and ongoing compliance costs.
The Advantages of Captive Power Plants
Captive power plants provide businesses with a significant strategic benefit by offering a dependable, affordable, and eco-friendly energy supply. But what are the advantages? Read more in this article!
Captive Power vs. Grid Power
Captive power generation and grid power serve distinct roles in energy provision. Captive power offers enhanced control, reliability, and potentially lower costs over time, particularly beneficial for industries in regions with unreliable grid power.
Conversely, grid power provides simplicity and convenience, with no upfront capital investment required and no need for ongoing operational management. However, reliance on the grid can expose businesses to energy price volatility and supply disruptions, which captive power generation avoids by producing energy independently of the public utility grid.
PowerUP for Captive Power Generation
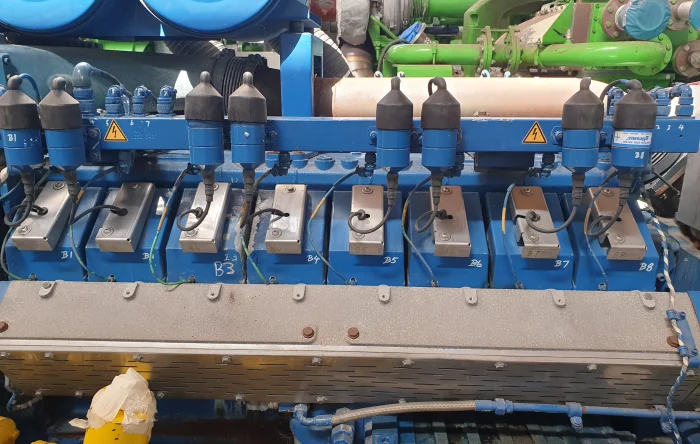
PowerUP offers specialized services for Captive Power Generation, providing tailored gas engine solutions that enhance both the efficiency and reliability of your captive power system. PowerUP supplies high-quality gas engine parts and services, like gas engine repair or a container solution, to ensure that your plant meets the demands of modern energy production. If you are looking for a gas engine, you can also buy an engine at PowerUP.