Contact us
Please fill in the form to contact the PowerUP expert team.
We are also happy to answer your questions by phone or e-mail.
Sportplatzweg 2
6135 Stans, Tirol
Austria
UID: ATU71231268
Phone: +43 5242 64 666
E-Mail: office@powerup.at


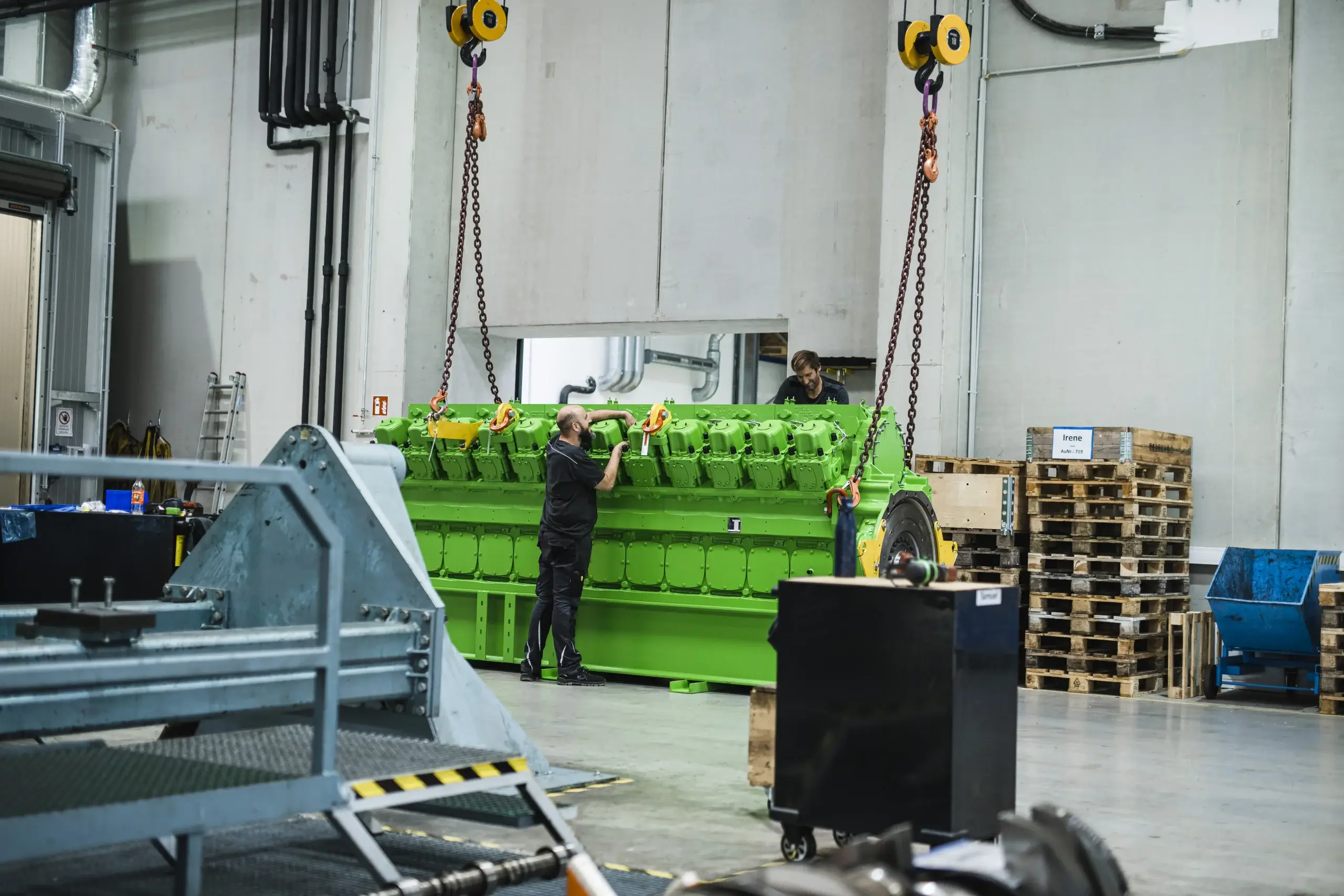
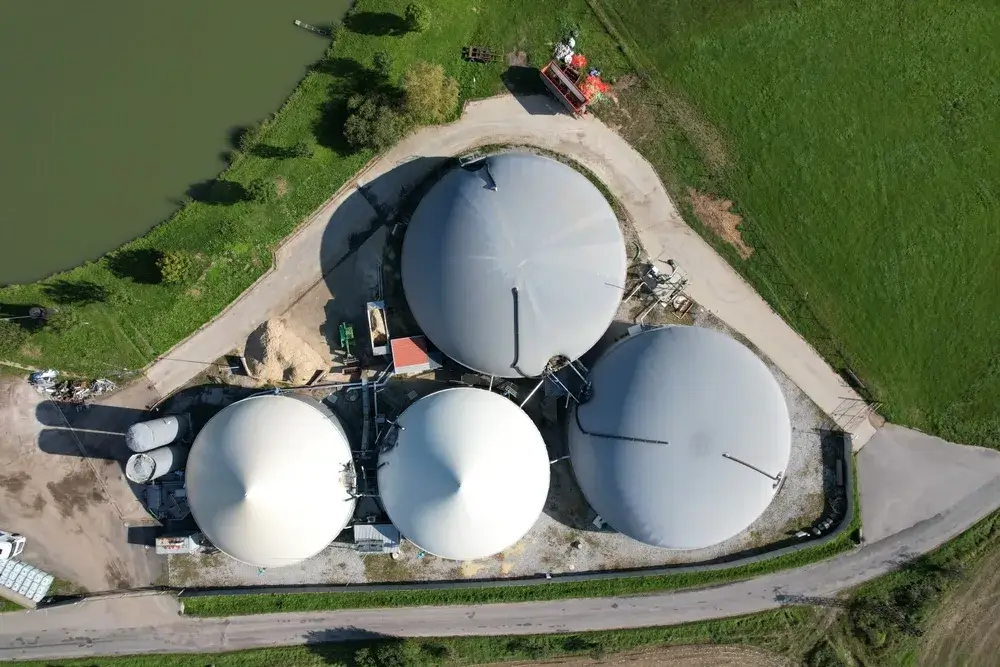
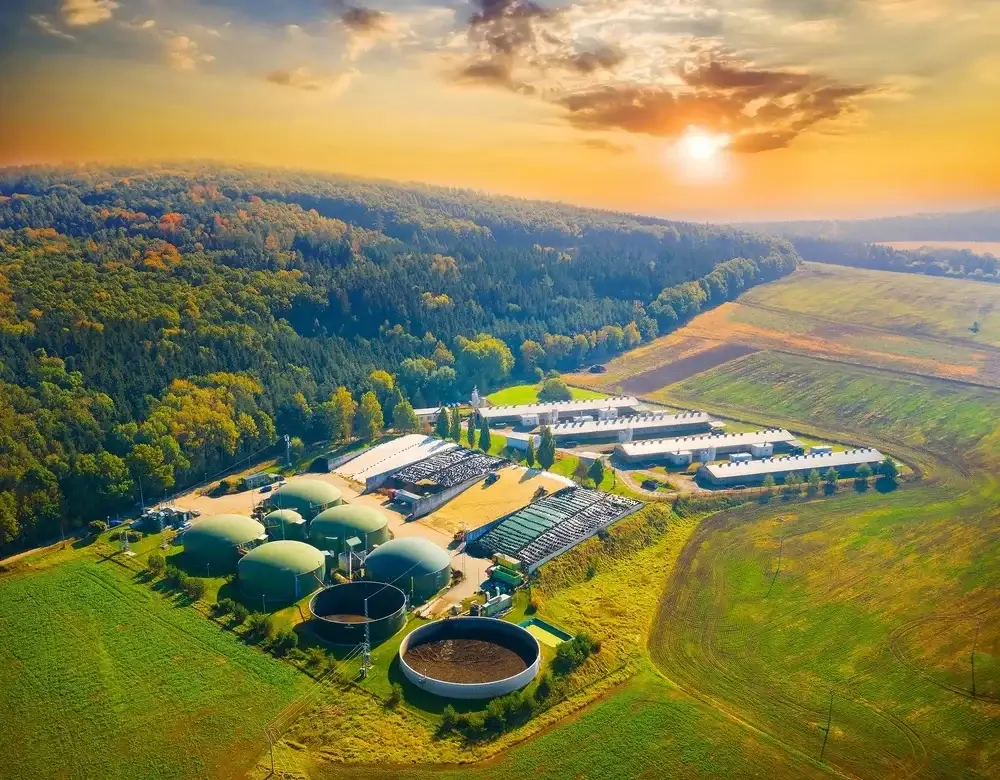
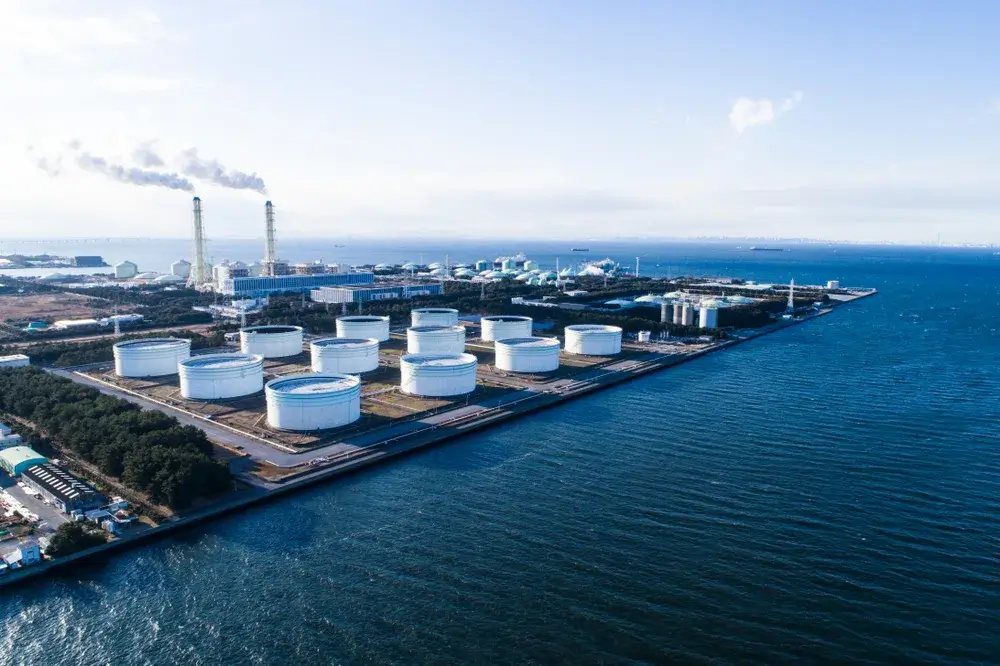
Welcome to the PowerUP Blog! Here’s where you’ll find the latest on innovations e.g. for gas engine updates, condition based overhaul, new gas engine spare parts or container solutions, and insights into the energy sector. From deep dives into biogas and natural gas to information and updates on Jenbacher® and MWM® engines, here you can power up your knowledge. Whether you’re in the industry or just energy-curious, join us as we explore the future of power together.















Please fill in the form to contact the PowerUP expert team.
We are also happy to answer your questions by phone or e-mail.
Phone: +43 5242 64 666
E-Mail: office@powerup.at

