What is meant by cogeneration?

Cogeneration is an innovative method of energy generation that efficiently utilizes not only electrical energy but also heat. This technology plays a crucial role in reducing environmental impacts and enhancing energy efficiency.
In this article, we will extensively examine the concept of cogeneration and provide a detailed explanation of its functioning and benefits.
Functioning of cogeneration
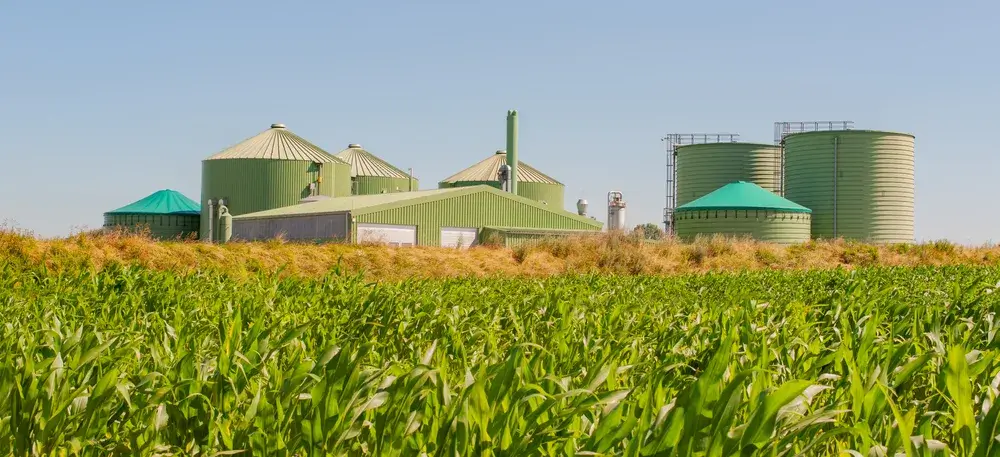
Cogeneration is based on the principle of simultaneously producing electricity and heat from a single fuel. This sets it apart from conventional methods, where the generated heat often goes unused.
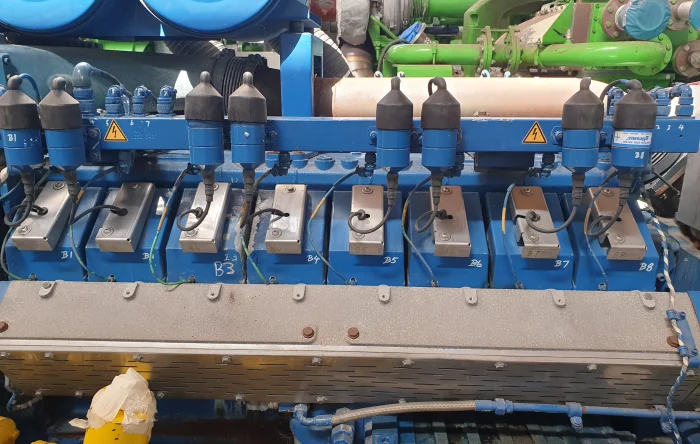
In CHP plants, the fuel, often natural gas or biogas, is burned in an internal combustion engine, a gas turbine or a steam turbine. This process generates mechanical energy that drives a generator and produces electrical power. However, as a by-product of the combustion process, waste heat is also generated.
Efficient utilization of waste heat
The key difference in cogeneration lies in the efficient utilization of waste heat. Instead of being discarded as an undesired by-product, it is purposefully captured and utilized for various purposes. This waste heat can be harnessed through heat exchangers to heat buildings, for hot water production or in industrial processes.
As a result, the overall efficiency of energy generation is significantly increased, as both electrical energy and heat are obtained from the same fuel.
Advantages of cogeneration
The advantages of cogeneration include a wide range of benefits, encompassing both environmental and economic aspects:
Reduced emissions
By efficiently utilizing the fuel and preventing the waste of unused heat, cogeneration plays a role in reducing CO2 and other harmful emissions. This contributes to improving air quality and supporting efforts to combat climate change.
Energy efficiency
The simultaneous generation of electricity and heat in CHP systems results in a significant increase in energy efficiency compared to separate electricity and heat generation methods. Cogeneration can achieve efficiencies of over 90 percent, while conventional power plants often achieve only around 40 percent efficiency.
Energy independence
The combined heat and power (CHP) technology can contribute to reducing dependence on external energy sources. This is especially beneficial during times of increasing energy prices and uncertainties in the energy supply.
Decentralized energy generation
CHP systems can be installed in a decentralized manner, which reduces the need for long transmission lines and the resulting energy losses. This contributes to stabilizing the power supply and relieving the pressure on the electricity grids.
Economic advantages
CHP can result in significant savings in energy costs, particularly when the generated heat is effectively utilized. Moreover, many countries offer governmental incentives and support programs that enhance the attractiveness of investments in CHP plants.
PowerUP® — Your partner for gas engines
With a range of gas engine solutions, PowerUP provides you with service and spare parts suitable for brands like INNIO Jenbacher®, MWM® and Caterpillar®. From specially designed gas engine spare parts to gas engine repairs, replacement engine, and even a container solution – thanks to our expertise in this field, our customers always benefit from the highest quality service.

Conclusion
Cogeneration is a forward-thinking technology that enhances the efficiency of energy production, mitigates emissions, and provides both environmental and economic advantages. By intelligently harnessing waste heat, it contributes to resource conservation and drives sustainable energy supply. In a time when environmental preservation and energy efficiency are of growing importance, cogeneration is rapidly gaining significance as a key technology.