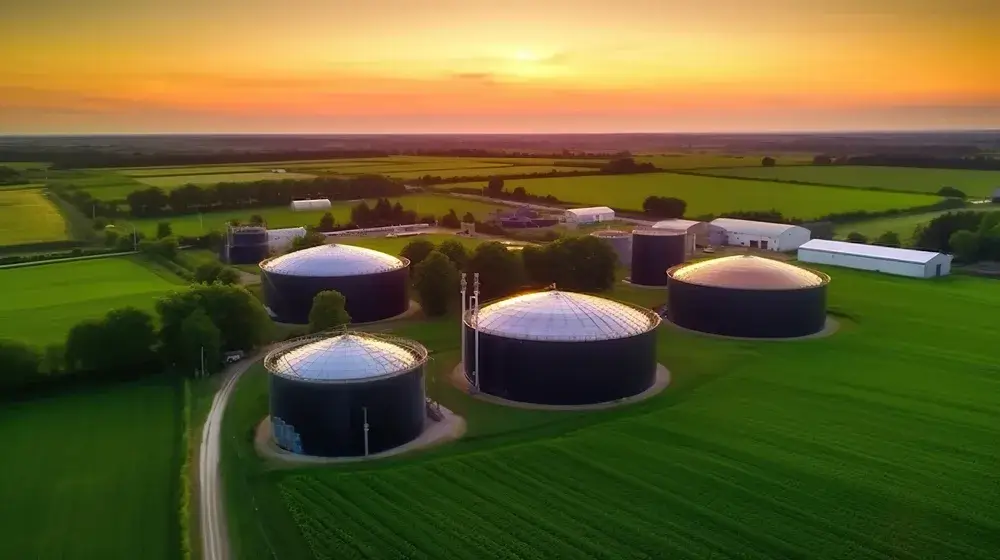
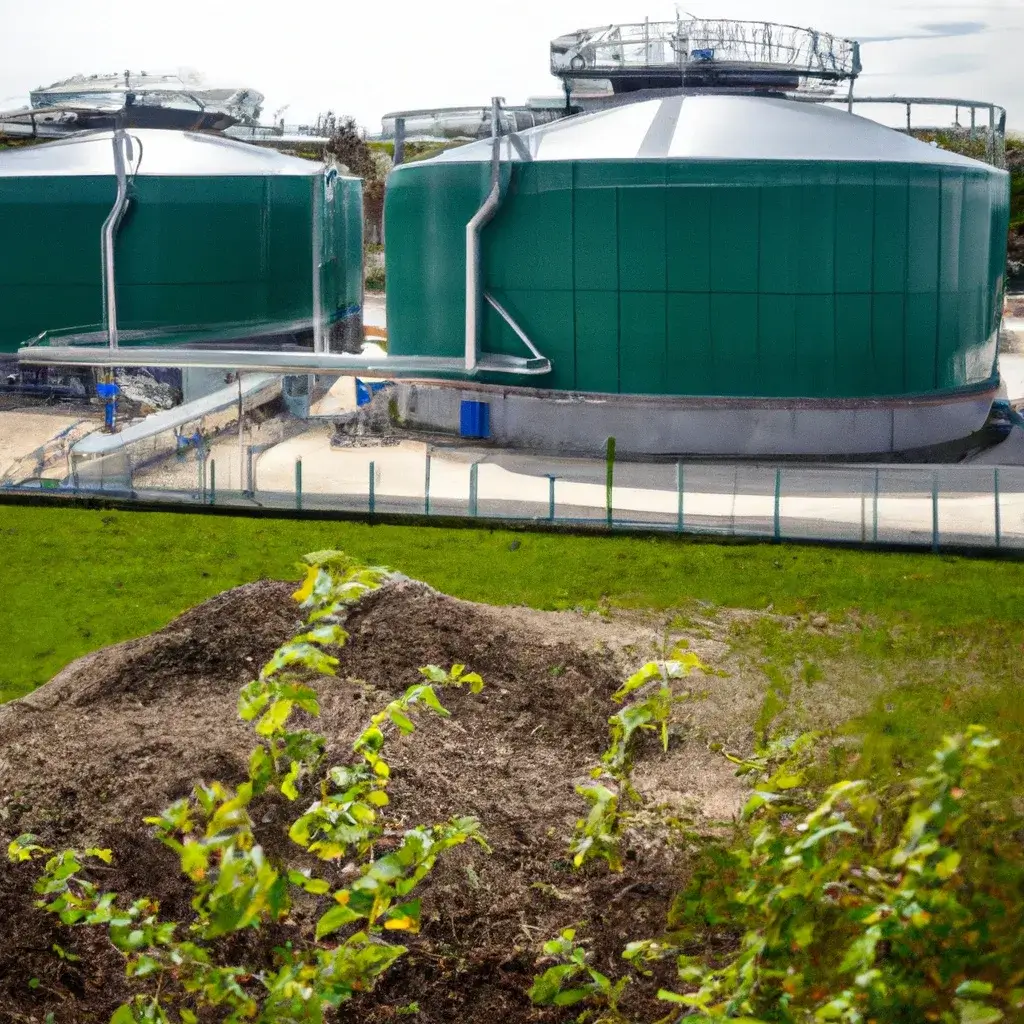
Biogas Plants – A Comprehensive Guide

Biogas plants are advanced technologies that make a crucial contribution to the generation of renewable energy. At their core, biogas plants are facilities that convert organic materials into biogas.
This form of energy generation not only offers an environmentally friendly source of energy but also supports the transition away from fossil fuels. Consequently, significant efforts are being made to enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biogas energy production and biogas farming.
The growing popularity and significance of biogas plants in the energy sector demonstrate their essential role in achieving a sustainable future. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the functionality, advantages, and challenges associated with this technology.
The history and development of biogas plants
The history of biogas plants and biogas production dates back far before the focus shifted to renewable energies. In earlier times, various cultures recognized the potential of gases formed through the decomposition process of organic materials.
However, it was not until the 20th century that technology and knowledge about the production of biogas advanced in an organized and optimized manner. Technological progress and the growing need to develop alternative energy sources led to more intensive research and further development in the field of biogas production.
Especially in recent decades, with the emergence of renewable energies and the increasing awareness of the environment, biogas plants have gained popularity worldwide. Since then, there has been a concerted effort to increase the efficiency of gas engines that are required for generating energy from biogas.
Today, biogas plants are an integral component of energy strategies in Germany and many other countries that aim to decrease the reliance on fossil fuels and create a more sustainable energy future.
The functioning of a biogas plant
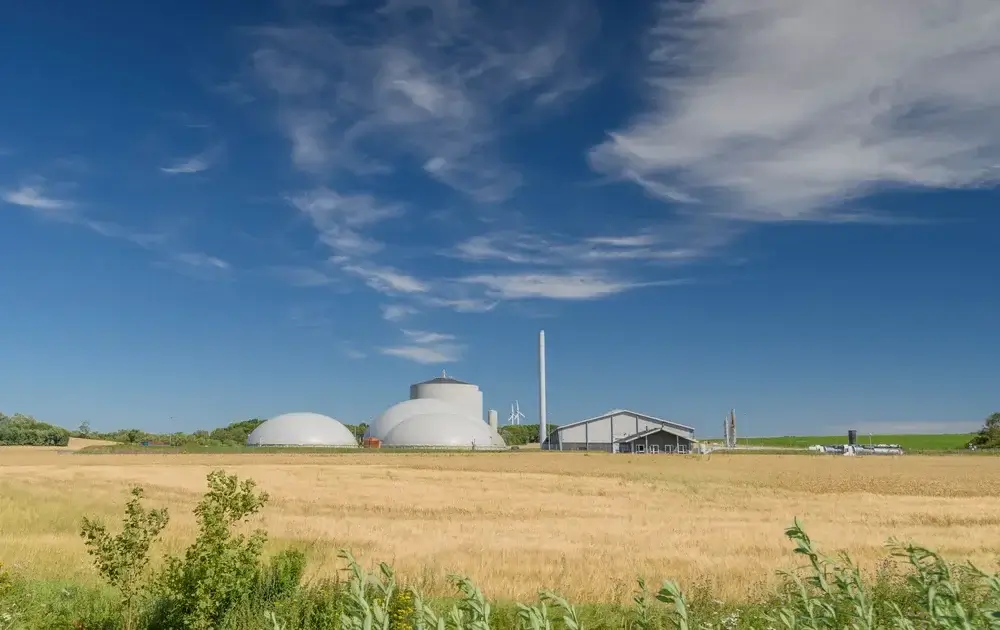
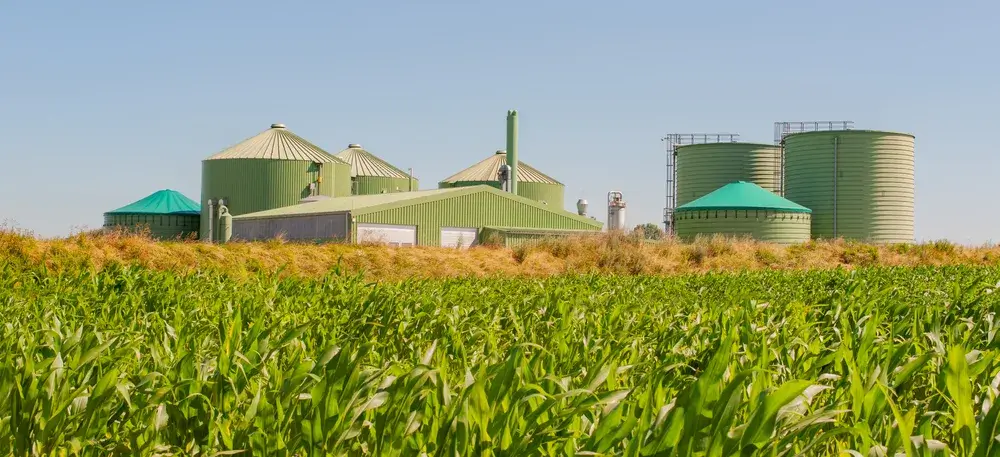
The function of a biogas plant is based on a complex process in which organic materials are broken down. At the core of the plant is the fermenter – a closed system where anaerobic microorganisms decompose the organic substances without the presence of oxygen.
How does a biogas plant function?
How does a biogas plant actually work? What are the various steps involved in the transformation of the starting materials into biogas? Continue reading to find out!
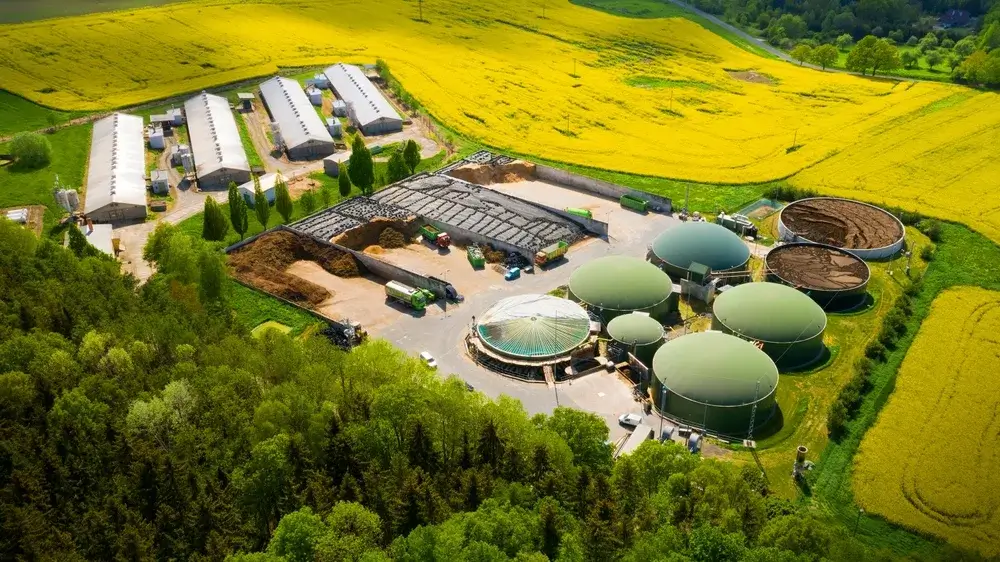
The main components of a biogas plant
The components of biogas plants work together harmoniously to optimize the fermentation process, extract valuable biogas from various organic materials and ultimately provide energy in different forms, such as heat or electricity. Therefore, every single component of a biogas plant is crucial for optimal function.
Feedstocks and their processing
The versatility of biogas plants is especially evident in the wide range of feedstocks that can be processed in them. Common feedstocks include manure, a by-product of livestock farming, as well as energy crops such as corn or grass, which have a high methane content. Specifically dedicated cultivation areas are used for these plants for the purpose of biogas production.
Additionally, organic waste, such as food waste and organic garden waste, can also be utilized as raw materials. The processing of these materials starts with their collection and subsequent introduction into the biogas plant.
In the pre-digester, the organic waste is shredded and homogenized, preparing it for the fermentation process. Through this anaerobic breakdown process, carried out in the absence of oxygen within the fermenter, the organic waste is ultimately transformed into methane and carbon dioxide.
Valuable gas is not the only thing being extracted; the organic materials are also recycled in a meaningful way, promoting a sustainable approach to resource management.
By-products and their applications
In the process of recycling organic materials in biogas plants, various valuable and usable by-products are also generated alongside the actual biogas.
An important by-product of a biogas plant is fermentation residues. These residues serve as a nutrient-rich fertilizer that can be utilized in agriculture. They contain essential minerals and trace elements, which contribute to the natural revitalization and increased fertility of the soil. This, in turn, reduces the reliance on artificial fertilizers.
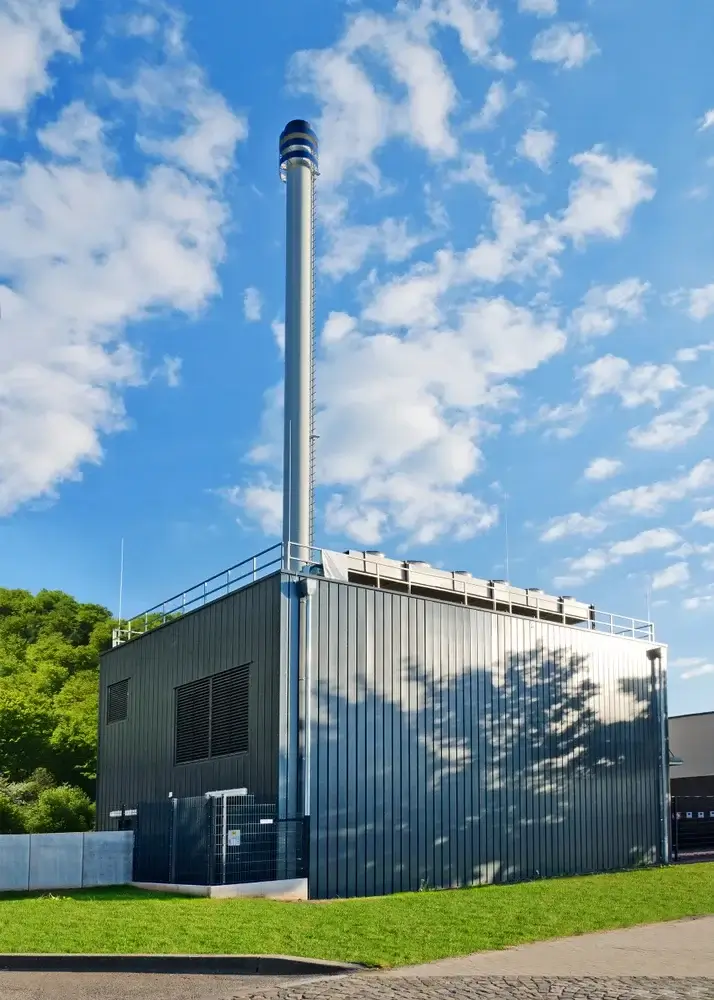

Furthermore, heat is generated during the process of fermentation, which can be utilized for heating purposes or for regulating the temperature of buildings. Another by-product is hydrogen sulfide, which, when produced in larger quantities, can be treated and used in various industrial applications.
The difference between biogas and natural gas
Biogas and natural gas are both gaseous fuels that can be used in many applications, but they differ in terms of their origin, composition, and environmental impact.
Biogas is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as manure, energy crops, and organic waste. It primarily consists of methane and carbon dioxide, but can also contain small amounts of other gases such as hydrogen sulfide. In contrast, natural gas is a naturally occurring gas that is predominantly made up of methane and is formed deep within the earth from fossil sources, such as deceased plants and animals.
An important difference also lies in the environmental impact. The production of biogas is considered sustainable and renewable because it is derived from renewable raw materials and utilizes carbon that was recently extracted from the atmosphere. On the other hand, natural gas is a fossil fuel whose combustion releases carbon that has been sequestered in the earth for millions of years.
However, when biogas is upgraded to natural gas quality, the carbon dioxide and other components are removed, resulting in biomethane that is chemically similar to natural gas. This allows for the injection of biomethane into the existing natural gas grid.
What is the difference between natural gas and biogas?
What is better — biogas or natural gas? In this article, we will look into their advantages and drawbacks. Biogas and natural gas are two significant energy sources that are utilized in different sectors for energy generation.
The injection of biogas into the natural gas network
The ability to inject biogas into the natural gas grid represents a revolutionary step in sustainable energy production. After the gas produced in the biogas plants has been processed to meet natural gas quality standards, it can be directly fed into the existing gas network.
This process of feed-in means that the biogas, now referred to as biomethane, is available for households, industrial applications, or even as fuel for vehicles, just like conventional natural gas. The treatment specifically removes components such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide from the biogas in order to achieve a quality that meets the high standards of the natural gas network.
The key advantage of injecting biogas into the natural gas grid lies in its high flexibility and the ability to utilize existing infrastructure. Moreover, it provides a renewable alternative to fossil natural gas and significantly contributes to reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Benefits of using biogas plants
Biogas plants are not only a significant component of the renewable energy sector, but they also offer a multitude of benefits that extend beyond just energy production.
The generation and utilization of energy
The generation of energy through biogas plants is a process in which the produced biogas is converted into usable energy. This is typically done in a combined heat and power plant (CHP), which combusts the methane in the biogas to generate both electricity and heat. This form of power generation represents a clean and renewable energy source that can be directly fed into the electricity grid or used on-site.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide emissions
On the one hand, they contribute significantly to reducing carbon dioxide emissions by replacing fossil fuels. They also promote the sustainable utilization of organic waste and by-products from agriculture, such as manure and crop residues. This contributes to the circular economy and helps reduce waste
- Supporting regional value chains
Biogas plants also contribute to regional value chains and generate employment opportunities in rural areas. They enable the production of clean electricity and heat, thereby enhancing the security and diversity of energy supply
- Possibility of feeding into the natural gas network
Finally, after proper processing, the biogas produced can be injected into the natural gas network as biomethane or used as a fuel, opening the path towards greener mobility.
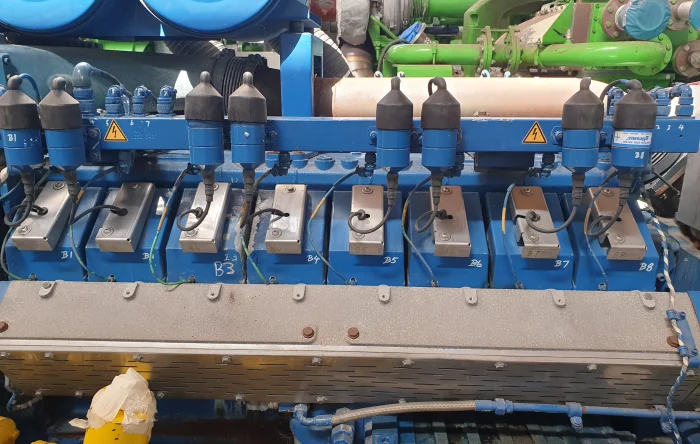
Gas engines are frequently utilized to convert biogas into usable energy. Particularly in areas with unreliable energy supply, these gas engines from manufacturers like MWM®, Caterpillar®, or INNIO Jenbacher® play a crucial role in regional energy provision. Consequently, the demands for efficiency and longevity of these gas engines are high, which are core competencies of PowerUP. PowerUP also extensively works on optimizing gas engines with their in-house solutions for PUP GEN.
In addition to direct electricity generation, the gas produced can also be treated to meet natural gas quality standards and injected directly into the natural gas grid. This process of injection ensures that the produced biogas is utilized optimally and contributes to the overall energy supply.
Additionally, the waste heat generated during power generation can be utilized in local heating systems, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of the system. The utilization of biogas as a renewable energy source offers a plethora of benefits and plays a vital role in diversifying and advancing the sustainability of our energy supply.
Utilize biogas efficiently – with PowerUP
Gas engines used for the combustion of biogas need to be not only highly efficient, but also low-maintenance and long-lasting. This is because costs are a crucial factor in any form of energy generation – if renewable energy sources are economically viable, they will be increasingly adopted.
Furthermore, gas engines provide energy security and stability in regions with unreliable electricity grids, benefiting both private households and industries. It is crucial that these gas engines operate reliably and require minimal maintenance in such areas.
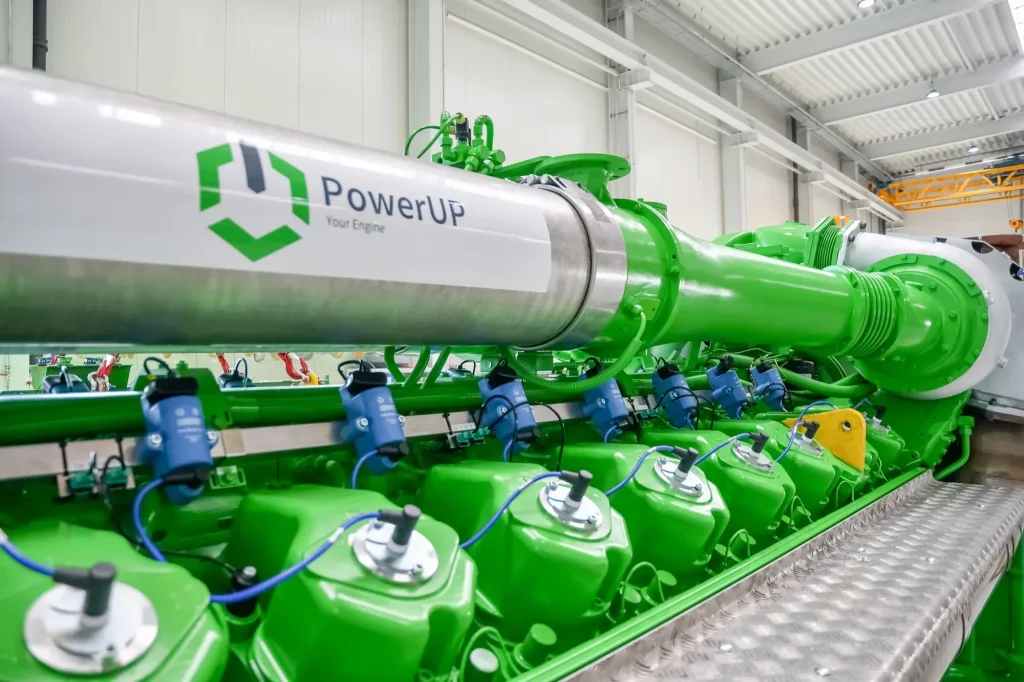

This is where PowerUP comes in – with worldwide, manufacturer-independent gas engine service and gas engine parts from reputable manufacturers such as MWM® or INNIO Jenbacher®. With the option for on-site installation as well as complete gas engine overhauls at our facility by skilled technicians, we ensure seamless maintenance work and greatly extend the lifespan of your engine. Additionally, our in-house solutions, such as the PUPGEN genset, further showcase our expertise.
With an additional emphasis on efficiency improvement, PowerUP also produces components for optimizing gas engines. These components not only enhance the efficiency of the engines but also streamline future maintenance, allowing the gas engine to remain productive for many operating hours.