Exploring the Advantages of Natural Gas

Natural gas has emerged as a critical energy source in today’s global landscape, bridging the gap between traditional fossil fuels and renewable energy. As a cleaner-burning fossil fuel, it offers significant advantages in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, making it a more sustainable option compared to coal and oil.
The natural gas industry has seen substantial growth, driven by advancements in extraction and production technologies. However, its role in addressing climate change remains complex. While natural gas contributes to lower carbon emissions, it is still a non-renewable resource, and its extraction and use pose environmental challenges.
What is Natural Gas?
Natural gas is a versatile energy source that consists primarily of methane, a hydrocarbon compound, along with other gases, like propane or butane. As one of the cleanest-burning fossil fuels, it is widely used for heating, electricity generation, and as a raw material in various industrial processes.
Formed from the ancient remains of marine organisms buried under layers of sediment and rock, natural gas is extracted from deep within the earth. Unlike coal and oil, which are also fossil fuels, natural gas emits fewer pollutants and greenhouse gases when burned, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
Natural gas – everything you need to know
Natural gas: Explore its role in energy provision, influence on global trade dynamics, and impact on geopolitical discussions.
How is Natural Gas produced?
Natural gas production may involve several processes, with hydraulic fracturing (fracking) being one of the most prominent techniques. Fracking involves injecting a high-pressure fluid mixture into shale rock formations to release the natural gas trapped inside. This method has significantly increased access to shale gas, a valuable resource found in abundance in regions like North America.
Once extracted, natural gas is transported via extensive networks of pipelines to processing facilities. Here, impurities are removed, and the gas is prepared for distribution. In some cases, natural gas is converted into Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) for easier and more efficient transportation over long distances. Last but not least, the gas is burnt in natural gas engines to produce energy and heat.
Advantages of Natural Gas
The use of natural gas offers numerous advantages, positioning it as a critical energy source. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Cleanest Fossil Fuel: Natural gas is the cleanest burning fossil fuel, producing significantly less carbon dioxide compared to coal and oil. This results in a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Lower Emissions: When combusted, natural gas emits fewer pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulates, contributing to better air quality and less environmental impact.
- Versatility: Natural gas is used in various applications, including electricity generation, heating, and CHP plants. Its versatility makes it a vital component in multiple sectors.
- Energy Efficiency: Natural gas is highly efficient in generating electricity and providing heating. Its efficient combustion process maximizes energy output while minimizing fuel consumption.
- Reliability and Infrastructure: The existing infrastructure for natural gas, including extensive pipeline networks and LNG facilities, ensures a stable and reliable supply. This infrastructure supports widespread use and accessibility.
- Economic Benefits: The abundance of natural gas, particularly with advancements in extraction technologies, helps keep energy prices relatively low and stable, benefiting both consumers and industries.
- Transition Fuel: As the world moves towards renewable energy, natural gas serves as an essential bridge fuel. It supports the gradual shift away from more polluting fossil fuels while renewable energy sources are scaled up.
These advantages collectively highlight why natural gas is a preferred energy source, offering a balance between environmental benefits and economic viability, and making it a cornerstone in the global energy mix.
Disadvantages of Natural Gas
While natural gas offers several benefits, it also has notable disadvantages. One significant concern is methane leaks, which can occur during extraction, production, and transportation. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential far greater than carbon dioxide, thus contributing significantly to climate change. Also, the leakage of carbon monoxide can be harmful.
Hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, used to extract natural gas, poses environmental risks, including potential contamination of groundwater supplies. This process involves injecting high-pressure fluids into shale formations, which can lead to the seepage of fracking chemicals into nearby water sources.
Additionally, natural gas is a non-renewable resource, meaning its reserves are finite and will eventually be depleted. This reliance on a non-renewable energy source delays the transition to sustainable and renewable energy alternatives.
Emissions and Climate Change
Natural gas, while cleaner than other fossil fuels, still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly through the release of carbon dioxide and methane. Statistics from the EIA show that when burned for energy, natural gas produces about 50-60% less carbon dioxide compared to coal, making it a more favorable option for reducing carbon footprints.
However, methane, a potent greenhouse gas, is often released during natural gas extraction and transportation processes, such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking). Methane has a global warming potential many times greater than carbon dioxide over a shorter time frame, significantly impacting climate change. Although natural gas is often promoted as a cleaner alternative, its full environmental impact must be considered, especially in terms of methane emissions, to truly assess its role in addressing climate change.
Cost-Effectiveness and Energy Efficiency
Natural gas is known for its cost-effectiveness and high energy efficiency, making it a popular choice for both residential and industrial energy needs. The abundance of natural gas reserves, especially in regions like California (North America), has led to relatively stable and low natural gas prices. This affordability translates into lower energy costs for consumers and businesses, providing economic benefits across various sectors.
Furthermore, natural gas power plants are highly efficient, often achieving energy conversion rates of over 60%. This high efficiency means more energy is produced from each unit of fuel, reducing waste and lowering overall energy consumption.
As a result, natural gas plays a crucial role in maintaining affordable energy costs while supporting energy efficiency goals.
Technological Advancements and Infrastructure
The natural gas industry has seen significant technological advancements that enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. The development of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) technology has also revolutionized the industry by enabling the efficient transport of natural gas over long distances. LNG terminals and storage facilities are crucial infrastructure components that support this global distribution network.
Advanced pipeline systems ensure a reliable supply, minimizing outages and maintaining consistent delivery to consumers and businesses. These pipelines, coupled with state-of-the-art storage facilities, help manage supply and demand fluctuations, ensuring stability.
Additionally, technological advancements on natural gas engines have led to significant emissions reductions, with modern processing methods designed to minimize greenhouse gas emissions.
The Role of Natural Gas in the Energy Transition
Natural gas plays a pivotal role as a bridge fuel in the global energy transition towards more sustainable and renewable energy sources. Its cleaner-burning properties compared to other fossil fuels make it a valuable intermediary in reducing greenhouse gas emissions while renewable energy technologies continue to develop and scale. Natural gas supports the integration of renewable sources by providing a reliable and flexible backup that can compensate for the intermittent nature of wind and solar power.
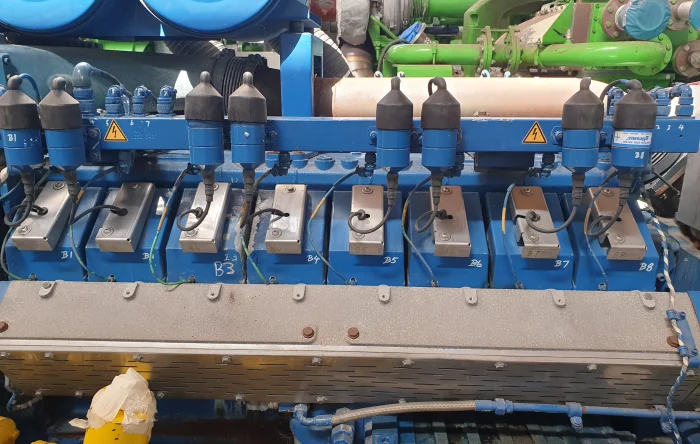
The long-term prospects of natural gas in the energy future depend on continuous innovation aimed at further reducing emissions and improving efficiency. Especially with natural gas engines, there is room for improvement. Companies like PowerUP help gas engine owners to improve the efficiency and sustainability of their plants with special gas engine spare parts and services.
PowerUP’s Gas Engine Services and Spare Parts
PowerUP specializes in providing gas engine services and high-quality spare parts, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Our comprehensive service offerings include condition based overhauls, gas engine upgrades or repair, and advanced diagnostics from our field service to keep your engines running at peak efficiency.

We supply a wide range of gas engine spare parts, including cylinder heads, pistons, spark plugs, and more, all designed to meet or exceed OEM standards. Utilizing PowerUP’s spare parts helps reduce downtime and maintenance costs while enhancing the overall performance of your engines.
Our commitment to quality and innovation ensures that we can support various industries with reliable and efficient solutions, making PowerUP a trusted partner in maintaining and optimizing gas engine operations.